clscripts
Repository for computational linguistics scripts (bash, python, octave, R, etc).
wordposition.sh
Get word locations in a given text file. The default behaviour is to show the word count position. It is also possible (and faster) to show the byte (char) position.
script usage
Use the script help to see the syntax and arguments.
$ ./wordposition.sh -h
Usage: ./wordposition.sh [option...]
-h, --help Display this help message
-o, --output-file Specify output file name
-i, --input-file Specify input file name
-b, --byte Use byte count to get a word position
-w, --word Word to search for
-c, --ignore-case Ignore case
usage examples
We present bellow the location of the word clock in Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland:
$ ./wordposition.sh -i alice.txt -w clock
14053
14334
14342
14363
14608
$ ./wordposition.sh -i alice.txt -w clock -b
79663
81407
81453
81569
83127
inter-token distance
The difference between consecutive lines in the previous result might be used to create a inter-token distance vector.
$ WORD='the'; ./wordposition.sh -i data/alice.txt -w $WORD | awk 'NR>1{print $1-p} {p=$1}'
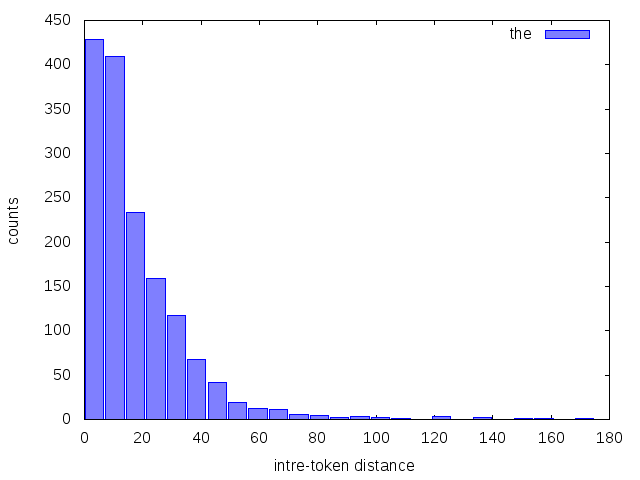
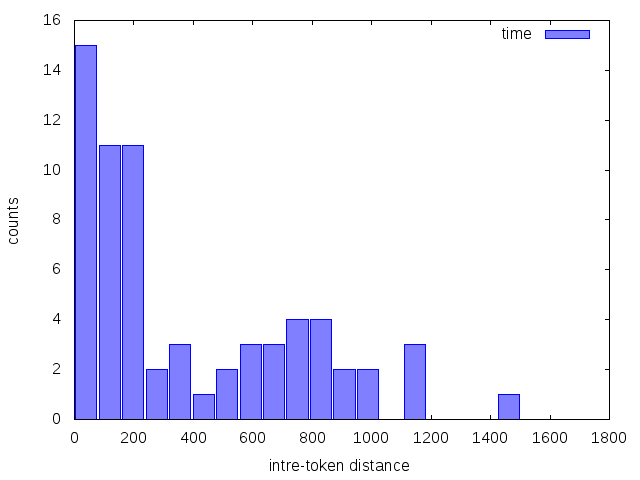
The result is further redirected to create a histogram of inter-token distance for a given word. We present two examples below, for the words: time and the.
$ WORD='time'; ./wordposition.sh -i data/alice.txt -w $WORD | awk 'NR>1{print $1-p} {p=$1}' | sort -n | gnuplot -p -e "numbins='25'; maxvalue='2000'; minvalue='1'; lbllegend='$WORD'; lblxlabel='intre-token distance'; lblylabel='counts'; outputfilename='$WORD-intertokenhist.png'" histogram.gp; display $WORD-intertokenhist.png
$ WORD='the'; ./wordposition.sh -i data/alice.txt -w $WORD | awk 'NR>1{print $1-p} {p=$1}' | sort -n | gnuplot -p -e "numbins='25'; maxvalue='200'; minvalue='1'; lbllegend='$WORD'; lblxlabel='intre-token distance'; lblylabel='counts'; outputfilename='$WORD-intertokenhist.png'" histogram.gp; display $WORD-intertokenhist.png